ONT – Classification, Marking, NBAR
Catégorisation du trafic faite grâce à des descripteurs:
- Ingress interface
- CoS Value on ISL or 802.1p frame
- Source or Destination IP Address
- IP precedence or DSCP value on the IP Packet header
- MPLS EXP value on the MPLS header
- Application type
Layer 2 QoS
Ethernet (802.1=q/p)
-
- Class of Service (CoS)
- On 802.1P frame
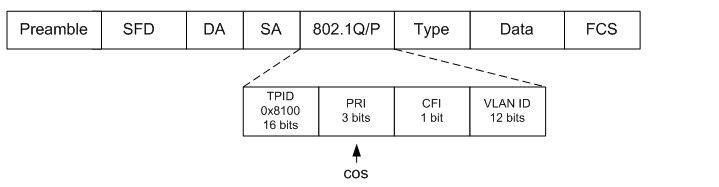
- 3-bit priority (PRI) field
- 000 – Routine – Best-effort
- 001 – Priority – Medium priority
- 010 – Immediate – High priority
- 011 – Flash – Call signaling
- 100 – Flash-Override – Video conferencing
- 101 – Critical – Voice bearer
- 110 – Internet – Reserved
- 111 – Network – Reserved
- Class of Service (CoS)
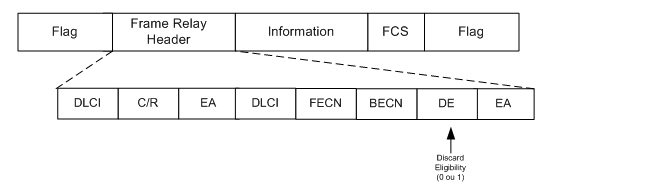
Frame Relay
-
- 1-bit discard eligible (DE) field
ATM
-
- 1-bit cell loss priority (CLP) field
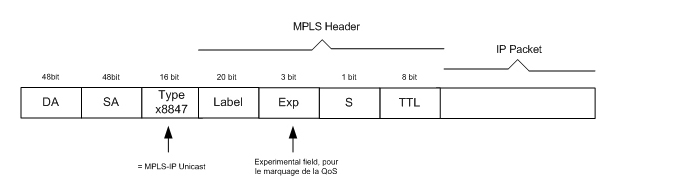
MPLS (layer 2 1/2)
-
- 3-bit experimental (EXP) field
- By default, the 3 most significant ToS bits (IP Precedence bits) are copied to EXP
- Per-hop Behavior (PHB)
- “Un comportement visible de transmission d’un noeud réseau vers un groupe de paquets IP qui ont la même valeur DSCP”
- On traite les paquets DSCP de même valeur de la même manière – (scheduling, queuing, policing, etc.)
- Behavior aggregate (BA) = Groupe que paquets IP avec la même valeur DSCP
- DSCP
- DSCP est réparti en 4 PHBs
- Class selector PHB – (000) old IP precedence compatibility
- Default PHB – (000) best effort
- Assured forwarding (AF) PHB – (001, 010, 011, 100) BW garantie
- 4 queues pour 4 classes de traffic (AF1-4)
- Also specifies drop preference (ex., AF41, A13) second numéro est la préférence (higher = probable to be dropped)
- Each queue must have (W)RED to avoid drops
- No queue is any better than the other
- Backward compatible with IP precedence
-
- Expedited forwarding (EF) PHB – (101) low delay
- Minimum delay
- Bandwidth guarantee
- Policing
- Expedited forwarding (EF) PHB – (101) low delay
- DSCP est réparti en 4 PHBs
- Trust boundaries
- Establish DSCP values au plus près de la source
- Sur l’équipement (IP phone), Access switch, ou Distribution switch
- Pas d’assignation de DSCP values au coeur du réseau
- Only trust DSCP values from devices you trust
- Examine and rewrite values from untrust sources
- Establish DSCP values au plus près de la source
- NBAR (Network-based Application Recognition)
- Protocol discovery – Découvre quel protocole fonctionne sur le réseau
- Traffic statistics collection – Fait des statistiques sur chaque protocol
- Traffic classification – NBAR peut être utilisé dans les class-maps pour déterminer le traffic intéressant
- Packet description language models (PDLMs) – Table des protocoles reconnus par NBAR
- Limitations
- Doesn’t work on EtherChannel interfaces
- Only handles 24 URLs, hosts, or MIME types
- Only analyzes first 400 bytes of the packets
- Need CEF
- Doesn’t work on HTTPS, multicasts, or fragments
- Ignored traffic destined for the router itself
- NBAR commands
Router(config)# ip nbar pdlm pdlm-name //Met à jour la table PDLM Router(config)# ip nbar port-map protocol-name [tcp|udp] port-number // Ajoute une entrée à la table PDLM Router# show ip nbar port-map protocol-name // Visualise la table PDLM Router# show ip nbar protocol-discovery // Visualise ce qui à été découvert Router(config-cmap)# match protocol name // class-map match match pour le protocole NBAR-discovered
- Special protocol matching
- Can match beyond the port number with deep packet inspection
- Matches HTTP hostname, URL, or MIME type
class-map from-cisco match protocol http host cisco class-map whats-up match protocol http url /latest/whatsnew* class-map jpeg match protocol mime "*jpeg"
- Matches fast-track P2P
class-map fasttrack1 match protocol fasttrack file-transfert "*" class-map fasttrack2 match protocol fasttrack file-transfert "*.mpeg"
- Matches RTP content
class-map voice match protocol RTP audio class-map video match protocol RTP video
Benoit
Network engineer at CNS Communications. CCIE #47705, focused on R&S, Data Center, SD-WAN & Automation.


